For an EV, batteries and motors are the main components. Using them right is very important. Therefore, you need to know about the motors used in EV.
There are a bunch of motors available in the market. But manufacturers mainly use BLDC, BDC, or AC induction motors.
Let’s see them now.
Table of Contents
BDC (Brushed DC) Motor
Brushed DC motors are being used for several applications since a long time ago. As the name suggests, direct current supply powers them.

You can see these motors serving a wide range of applications. From heavy-duty machines like cranes, rolling machines to tiny toys.
Also, these motors are very cheap.
This motor works with Flemings left-hand rule.
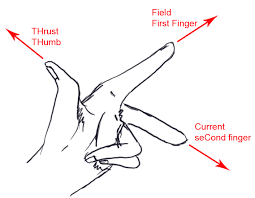
Stretch your thumb, forefinger and middle finger of your left hand. Now, your middle finger represents the direction of the current forefinger – the direction of the magnetic field and the thumb – the force applied.
The figure illustrates a BDC motor. I will cover more about this motor in a different article.
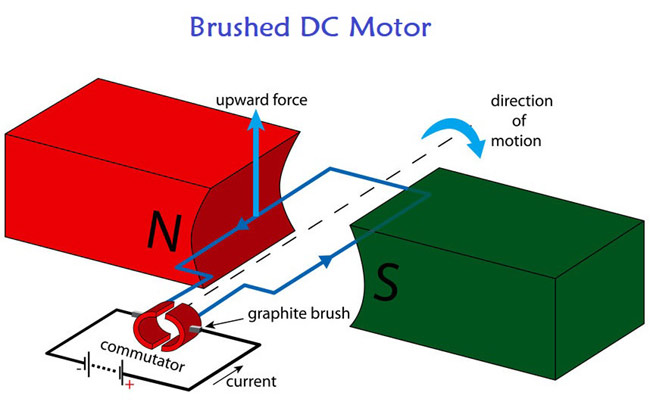
Though the motor is cheap, there is a brush that contacts the spinning commutator. Because of this, it generates a frictional force. This force reduces the efficiency of the motor as it generates excessive heat.
This leads to quicker wearing of parts and thus reduces the motor’s life.
BLDC (Brushless DC) Motor

This is a relatively new technology in the market. As I mentioned, the brush in the BDC motor is reducing its efficiency.
For an EV, there is no compromise on efficiency as it helps us to fight range anxiety.
Therefore, people use BLDC motor in their EVs. These motors are very much similar to BDC motors, but they do not have the brush.
Wait!!! There is yet another difference.
Unlike a BDC motor, a BLDC motor has its coils in the stator. And we place permanent magnets in the rotor.
Working
Assume a simple construction as shown.
This figure has a permanent magnet mounted on the rotor. And the stator has windings. To spin the rotor, I need to produce a magnetic field.
This is simple, pass DC current to the windings and done. But If I do this, I won’t be able to spin the motor as the force produced by a winding will be cancelled by the other windings.
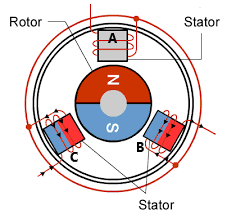
But what if I supply the current in a sequence? First coil A, then B and C.
Yes!! this is exactly how it works.
But there is a problem here. How do I achieve this sequence?
Unfortunately, you cannot do this easily as would need an electronic switching device. This means the motor won’t work if you connect the motor to a battery directly.

You can increase the speed of this motor can by increasing the switching frequency. But there is a certain limit beyond which if you increase the speed, the motor would halt abruptly.
This is because the frequency is so high that the circuit charges all the windings simultaneously. There is no time gap to differentiate the cycle.
Also, the motor is expensive.

AC induction motors

Many manufacturers use AC induction motors to power their EVs. This is mainly because of their low price, long life and low maintenance.
These motors have high starting torque but as we increase the load, speed decreases.
Also, batteries store energy in DC, but these motors need AC supply. Therefore, you may need an inverter which adds up to the cost and weight of the vehicle.
These motors also have good efficiency.
By varying the voltage or frequency, you can control the speed of the motor.
The working is like a BLDC motor. Instead of using an electronic switch, we use a 3 phase or a single-phase supply connecting each winding.

Switched Reluctance motor in EVs

Switched reluctance motor uses the principle of force generated because of magnetic reluctance.
The construction comprises a stator which has windings and a rotor. Interestingly, the rotor does not contain magnets or coils. But it is made up of laminated steel and it has poles as shown below.
When we energise the stator windings in a sequence just like BLDC motors, it generates a magnetic force. This force pulls the pole of the rotor.
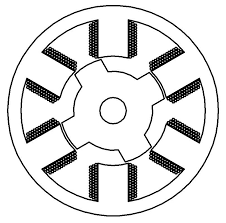
The number of teeth (or poles) in the rotor is more than the number of poles in the stator or the vice versa. We have to do this because this provides a self-starting capability to the motor.
Imagine the case where the number of poles is the same. If the poles and teeth are aligned, no matter which pole you energise, the rotor won’t move.
These motors are used in EV because of their ruggedness. This motor can handle high speeds and is definitely suitable for EV. Also, they are relatively cheaper.
However, they are noisy.
Permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM)
This is another option for manufacturers. The working of this motor is very similar to a BLDC motor, but the field windings use AC supply.
Unlike traditional synchronous motors, PMSM is self-starting. Compared to BLDC motor, these motors are noiseless.
These motors are made of rare earth materials. This increases their cost.
Also checkout Different types of electric vehicle in the market
